SAP makes software.
That’s the shortest SAP definition, but it’s not very useful.
So, if you would like to learn the complete definition of SAP in business terms and get a step-by-step explanation of SAP, this article is for you.
Keep reading!
The Definition of SAP in Business Terms Step-By-Step
The definition of SAP in a business context (not the plant fluid) is:
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) SE (Societas Europaea) is a European worldwide operating software company that makes software for the management of business processes suitable for organizations of any size and industry.
Let’s break this definition down, step-by-step:
#1 SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing)
SAP stands for “Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing” and “Anwendungen und Produkte in der Datenverarbeitung” in German.
When SAP was founded in Germany in 1972 by five former IBM employees, SAP stood for “Systemanalyse und Programmentwicklung”, later abbreviated to SAP. That German translates to “System Analysis and Program Development” in English.

In 1976, SAP changed the name to what it is today, probably because they anticipated going international soon and the previous full name didn’t work in English.
#2 SE (Societas Europea) is a European
SAP is a Societas Europea (SE).
Societas Europea is a Latin term that translates to “European society.”
A Societas Europea is a public company that is registered in accordance with the corporate law of the European Union.
When SAP was founded, it took the form of a private partnership (GbR) under the German Civil Code.
Then, in 1976, in accordance with German law, SAP founded a limited liability company (GmbH) that SAP turned into a stock company (AG) in 1988.
Finally, in 2014, SAP AG became a Societas Europea (SE) in 2014 and therefore transformed from a German company into a European company.
#3 Worldwide Operating Software Company
In 1977, SAP got its first international customers from Austria and France—5 years after SAP’s founding.
Today, SAP operates worldwide and has customers in 180+ countries—quite an impressive number since there are 196 countries in the world.
Software is that part of your laptop or mobile phone that you can’t touch; it’s the applications that perform calculations, record, return, and display information to you as a user.
The counterpart to software is hardware.
Hardware is the parts of your computer or phone that you can touch, things like the memory in your phone, the processor, the screen, and the device itself.
SAP doesn’t make hardware.
#4 That Makes Software for the Management of Business Processes
Software companies usually specialize in a particular kind of software, and SAP is no exception.
SAP makes business software that companies use to manage their business processes.
Imagine a business process as a flow of information and work needed to make something happen.
Almost anything can be described as a process.
To make a process more tangible, think of it like a flowchart.
For a personal scenario where you want to use your laptop:
- Locate the laptop
- Get the laptop
- Open the laptop
- Press the power button. If the battery is empty, plug the laptop into its power source.
- When the operation system is started up, then enter your credentials.
So a business process for a help desk might be:
- Answer call
- Create ticket
- Log details in the ticket
- Assess urgency and impact
- Assing priority
- Assign help desk employee to the ticket
- Help desk employee picks the highest priority ticket
- Help desk employee takes care of the ticket. If the help desk employee can’t take care of the ticket, then he escalates the ticket to a 2nd level help desk employee.
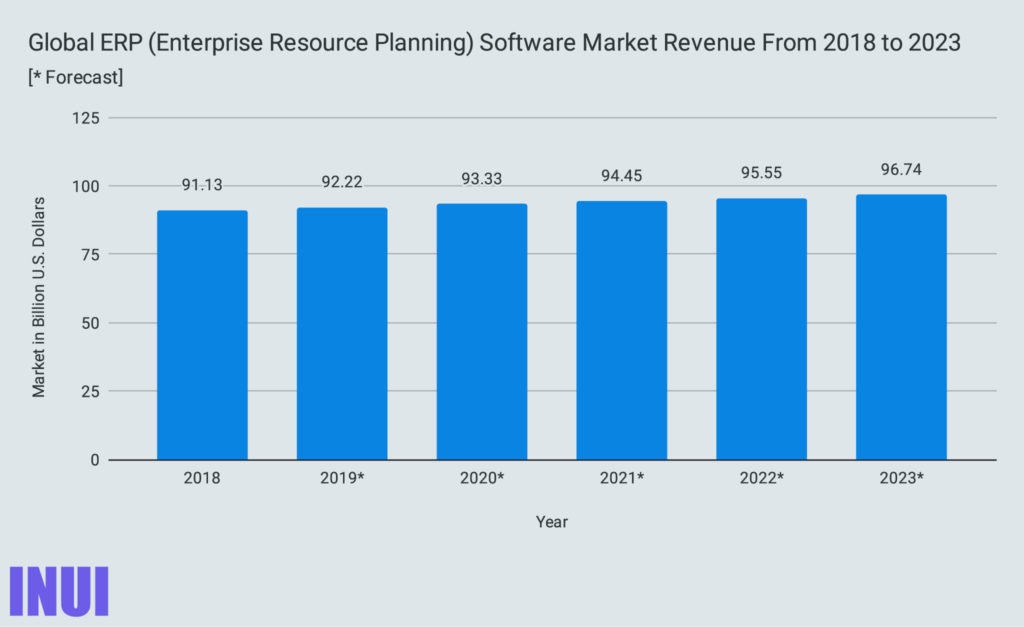
SAP is #1 in the ERP software market worldwide.
The ERP software market is expected to bring in 96.74 billion dollars worldwide by 2023:
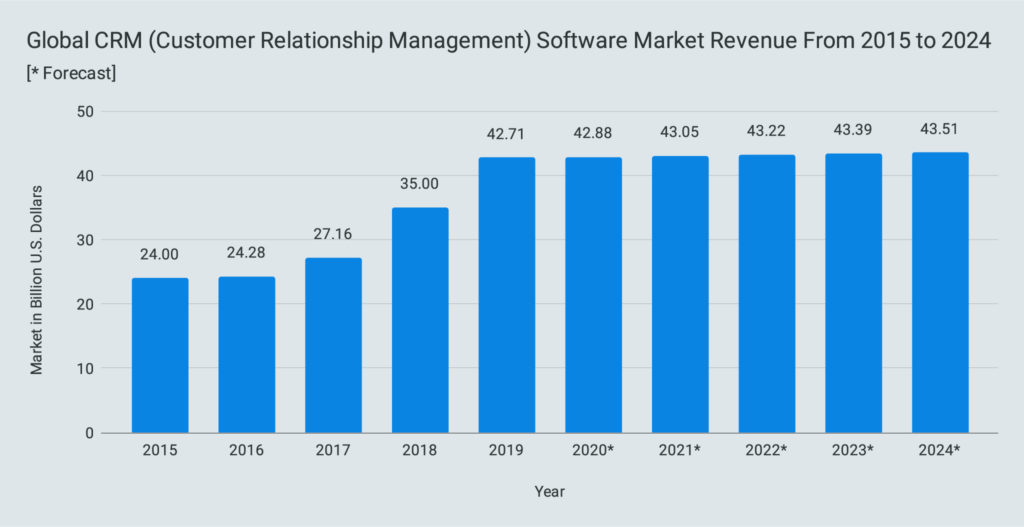
ERP software is divided into subcategories including SCM (Supply Chain Management), PLM (Product Line Management), and CRM (Customer Relationship Management). The CRM market is the largest among them:
CRM software is used to manage customer interactions, like running an online store and communicating with customers. CRM software is predicted to generate revenue of 40.26 billion US dollars by 2023:
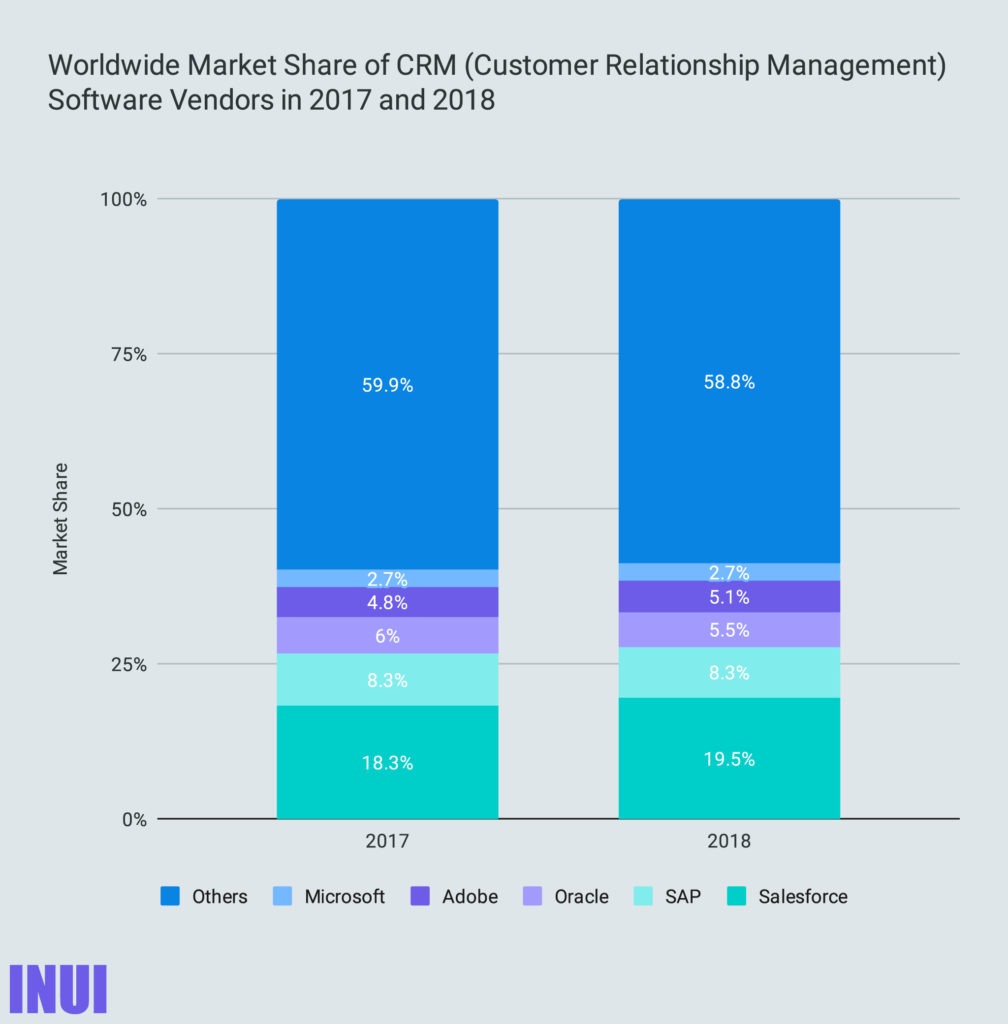
SAP is the second biggest CRM software company in the world behind Salesforce:
#5 Suitable for Organizations of Any Size and Industry
SAP’s business software solutions suit organizations of any size, from small startups to the world’s largest conglomerates.
Apple, the world’s largest company by market value, uses SAP products to keep track of all its orders on iTunes.
[Wikipedia]
Companies can customize SAP software to meet their needs.
An excavator manufacturer isn’t the same as a bank and so they need different software.
SAP software can be customized to meet these needs.
SAP also offers industry-specific software. The company pre-configured their software for certain industries, including:
- Consumer Industries
- Agribusiness
- Consumer Products
- Fashion
- Life Sciences
- Retail
- Wholesale Distribution
- Discrete Industries
- Aerospace and Defense
- Automotive
- High Tech
- Industrial Machinery and Components
- Energy and Natural Resources
- Building Products
- Chemicals
- Mill Products
- Mining
- Oil and Gas
- Utilities
- Financial Services
- Banking
- Insurance
- Public ServicesDefense and Security
- Federal and National Government
- Future Cities
- Healthcare
- Higher Education and Research
- Regional, State, and Local Government
- Service Industries
- Cargo Transportation and Logistics
- Engineering, Construction, and Operations
- Media
- Passenger Travel and Leisure
- Professional Services
- Sports & Entertainment
- Telecommunications
The SAP ERP modules list includes all SAP industry solutions and SAP ERP modules.
Now for some numbers about SAP:
Remarkable SAP Key Figures
SAP has:
- 340+ products
- 100,330+ employees
- 200,000,000+ users
- 440,000+ customers in 180+ countries
- 80% of SAP’s customers are small and medium-sized businesses
- 78% of the world’s food is distributed by SAP customers
- 82% of the world’s medical devices are distributed by SAP customers
- 92% of the Forbes Global Companies are SAP customers
- 98% of the 100 most valued brands are SAP customers
- 97% of the greenest companies are SAP customers
77% of the world’s transaction revenue touches an SAP system.
[SAP]
SAP is the:
- #1 in the ERP software market worldwide
- #1 largest software company in Europe
- #2 in the enterprise application software market (Microsoft is #1)
- #2 in the CRM market (Salesforce is #1)
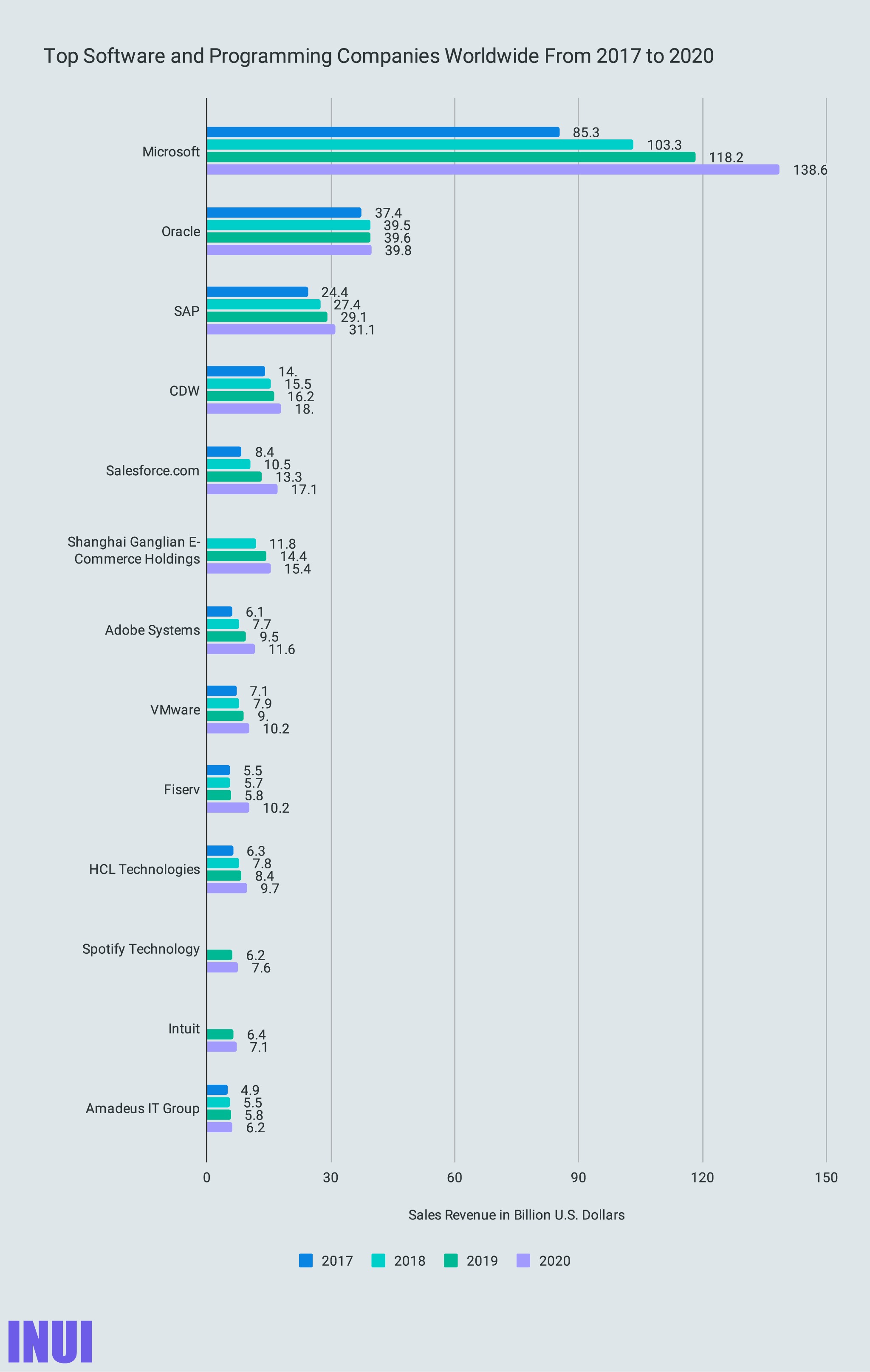
- #3 largest software & programming company worldwide
- #3 in the software & programming market overall
SAP has:
- €27.63 ($29.9) billion revenue
- €8.21 ($8.91) billion operating income
- €3.39 ($3.68) billion net income
- €60.22 ($65.36) billion total assets
- €30.84 ($33.47) billion total equity
SAP posted revenues of $29.2 billion in 2019. By comparison, Adidas’ revenue was $25.9 billion.
[Fortune]
See here for the complete SAP Facts list.
Anyway, what’s the bottom line?
Super Simple SAP Explanation
You’ve got a business.
Not just any business, but a big one.
Your company has grown so big that it has split into divisions such as accounting, human resources, and production.
Now, your business isn’t a business anymore. It’s an enterprise.
You need to connect every part of your enterprise to make your organization work as a whole.
For example, the sales department sells one of your products.
Accounting needs to know about the sale so they can send an invoice to the customer.
Additionally, production has to know that they need to make the product.
Then logistics needs to know it needs to ship the product to the customer.
On top of that, you have to be able to compare the price to previous sales, and you have to look at the time from sale to delivery compared to the last 1000 sales of that particular item.
You’ll also need sales data for that specific customer in the last 10 years.
It All Comes Down to Information Technology
You need to bring the different parts of your enterprise together and make it easy for your enterprise to share resources across divisions.
In the 21st century, you don’t want to use letters, carrier pigeons, and file archives.
In today’s world, you rely on digital IT (Information Technology).
IT uses applications instead of letters, servers instead of pigeons, and databases instead of files.
IT makes things faster and more efficient.
ERP Software ties everything together. SAP was one of the pioneers in this particular industry in 1972.
[SAP]
Imagine you urgently need a specific screw from a supplier because you run out of stock of it.
Your supplier is located at the other end of the world and it’s the only one who makes this type of screws.
If you don’t get that screw within three days then your project will fail that you worked on since ever.
So do you want to hire and send a messenger with the next ship with the destination other end of the world to your supplier hoping the messenger survives the journey and returns with the screw in perhaps a year or two?
Or just open the supplier’s online store, put the screw in your basket, select extra fast delivery, and push the order button to have the screw within two days in your letter box?
SAP makes the virtual part of IT
This is where SAP comes in.
SAP makes software for applications, servers, and databases.
SAP software combines, manages, tracks, and analyzes everything your business does to archive its goal, all in one place.
Currently, business software is not just for large companies, but for small businesses too.
Particularly since cloud computing applications are ready to go without a big up-front investment for hardware, licenses, and IT experts.
ERP is the biggest segment in business software. CRM is the largest subcategory of ERP in terms of market size and growth.
ERP software combines, manages, tracks, and analyzes everything a company does in order to archive its goals as a company such as human resources, finance, production, and customer management.
CRM focuses on intertwining, managing, tracking, and analyzing everything related to your enterprise and your customers. CRM manages things like customer data, online shops, and service tickets.
Short and sweet:
SAP is a HUGE company that makes software to manage business processes (SAP is #1 in the ERP software market and #2 in the CRM software market).