This is about SAP HANA.
SAP HANA is a relational database management system.
It’s super fast and has an embedded application server.
Let’s get started!
Understand SAP HANA
SAP HANA is an in-memory database for real-time processing of large amounts of data with a built-in application server. It’s SAP’s biggest mover and shaker.
SAP HANA is packed with features like:
- Column-based storage
- Data aging and dynamic tiering
- Data modelling
- High availability and disaster recovery
- In-memory
- Monitoring tools
- Provisioning capabilities
- Tons of security options
SAP HANA can be deployed:
- On-premise
- In the cloud
- Hybrid (on-premise and cloud).
If your organization has been looking for a robust database solution that can scale with your business, there’s a good chance that SAP HANA is what you’ve been waiting for.
One of the most powerful database management systems on the market, SAP HANA has been growing in popularity over the past decade due to its innovative in-memory data processing and other innovations.
See, there’s a reason SAP HANA stands for High-Performance Analytics Appliance.
This guide will provide you with an in-depth look at SAP HANA and how it streamlines business processes, providing instant data processing and analytics, and bringing innovations to the newest generation of SAP ERP applications.
SAP HANA Overview
Before delving into detail about SAP HANA’s features and what it can do for your business, it might help to start with a bird’s-eye view of the product so that you understand what it is and where it fits in the realm of business software.
Once you have a better idea of what SAP HANA is, you’ll be better able to appreciate how far it’s come and how truly innovative its features are.
So let’s start at the beginning with a quick introduction to the makers of SAP HANA:
Who Makes Sap HANA?
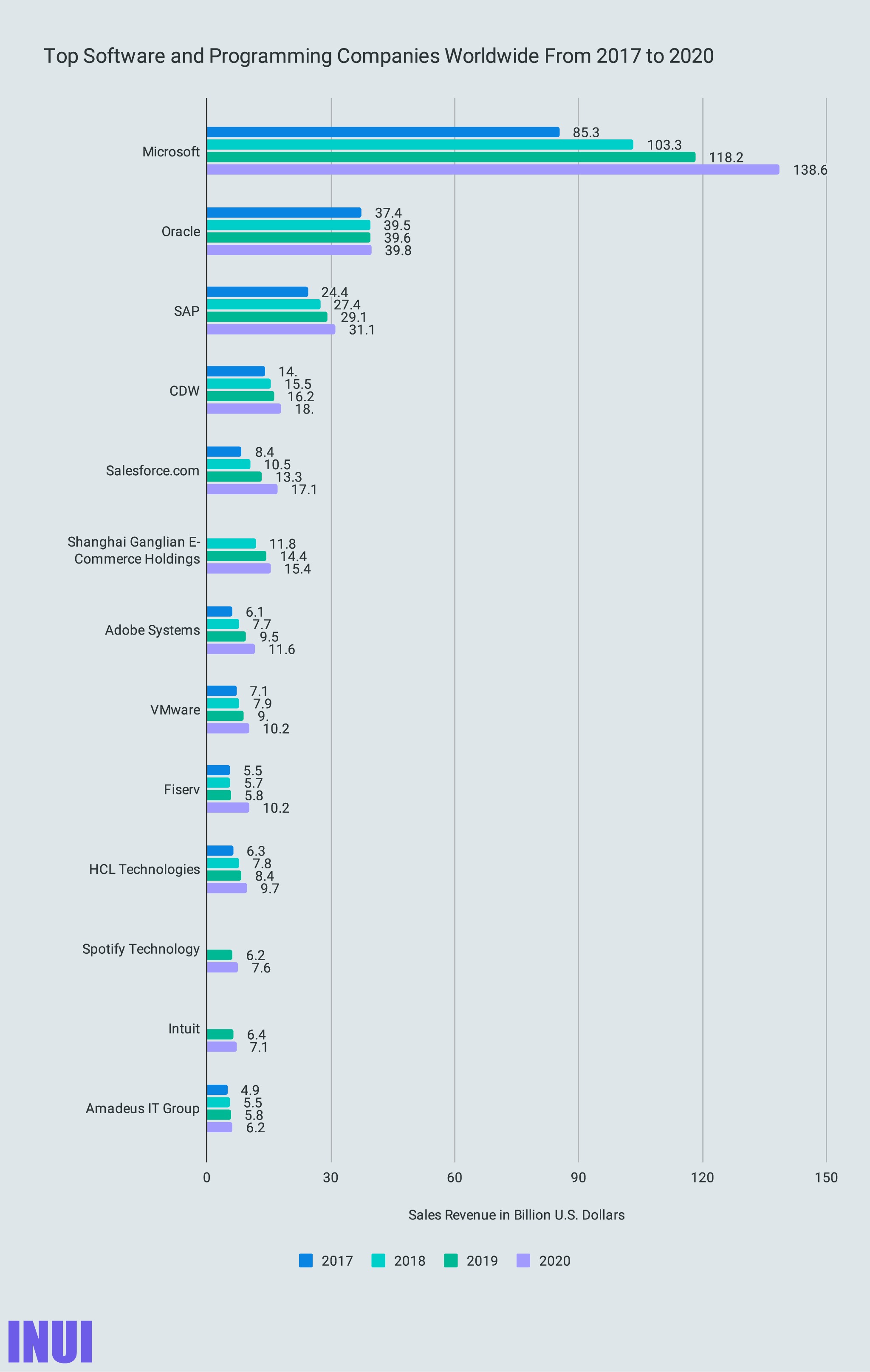
SAP HANA is made by SAP, which is the 3rd largest software and programming company worldwide. They are based in Germany and make enterprise software, which includes handling all kinds of business processes.
SAP stands for Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing.
The SAP definition is:
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) SE (Societas Europaea) is a European worldwide operating software company that makes software for the management of business processes suitable for organizations of any size and industry.
In a nutshell, SAP makes ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software.
ERP software is software that’s designed to help businesses and other organizations run effectively.
An ERP is a business process management system that manages and standardizes business processes to effectively plan and control the business and deliver competitive advantage.
ERP software contains components, or modules, each of which allows workers to handle functions of a particular department or business process, like:
- CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
- Finance
- HR (Human Resources)
ERP is different from other kinds of business software like a basic accounting software or a ticket system:
One of the key features of ERP is how modules are integrated and communicate with each other. For example, sales orders created in CRM will be shared with production so they know what products to make. After the product is shipped, data changes in the inventory management module, and the revenue is logged in the accounting module after the customer pays.
In its simplest form ERP software is all about management of business processes.
In current times it’s increasingly common for businesses to be spread out across a state, country, or even the world. Enterprise software can help centralize and simplify data collection and storage and allow it to be used across teams in multiple locations.
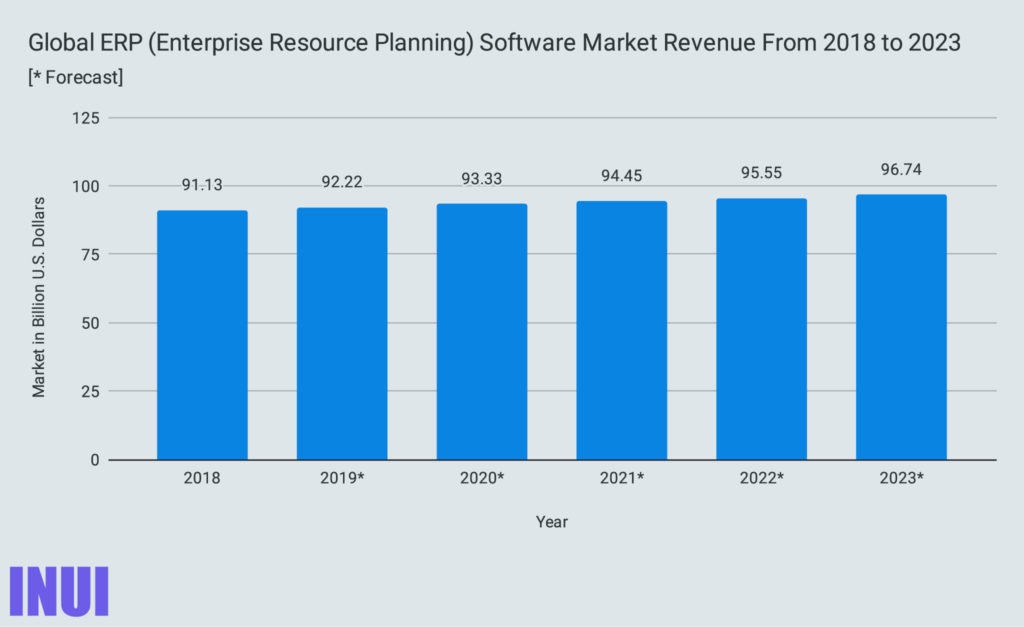
ERP is a HUGE market that keeps growing every year. It’s about to hit $100 billion soon. For comparison, the global entertainment industry (theatrical and home entertainment) has a market of $100 billion.
What Is SAP HANA?
SAP HANA is an RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) and application server with robust analytical and ETL (Extract, Transform, and Load) capabilities.
So SAP HANA has nothing to do with ERP software at first glance. It’s just a database, isn’t it?
No, it is not. SAP’s most recent ERP applications such as SAP S/4HANA and SAP CX (formerly SAP C/4HANA) are built on and rely on HANA.
You literally can’t say SAP S/4HANA without HANA. Same for almost any new SAP application. No matter if it has HANA in its name or not.
SAP HANA is more than just a database for your newest side project to automate your cat’s feeding. SAP HANA is one of the core components that make SAP’s latest generation of ERP applications to what they are in terms of innovations and new features.
Let’s take a look:
SAP HANA Is an RDBSM (Relational Database Management System)
Databases store data about products, customers, orders and other aspects of business operations for use in transaction processing and analytics applications.
SAP HANA is a DBMS.
DBMSs (Database Management Systems) support the development, management and use of databases. DBMS is a blanket term for database management technologies developed over the last 50 years.
In the 1960s, the first database management systems supported hierarchical databases, in which data was organized into trees with parent and child records, and network databases. Data elements were mapped to each other in multiple parent-child groups.
SAP HANA is an RDBMS.
A RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) was developed in the 1970s and then emerged as the most popular database technology. Its key features include its table structure and support for SQL (Structured Query Language). SQL is a programming language for managing relational databases and getting data from them.
RDBMS are based on the concept of database normalization. Database normalization means putting your data in tables so that the results are always unambiguous and as you intended them to be.
RDBMS establishes relationships between rows of data in different database tables based on the restrictions of primary and foreign keys.
Primary keys are identifiers that are unique per table row. For instance, a material number might be the primary key for a table with materials. Foreign keys point to other tables’ primary keys.
The ability to link related data values using keys eliminates the need to store data in one table. This reduces data redundancy, reducing storage requirements, streamlining maintenance and enabling faster querying in RDBMS environments.
An RDBM lets organizations of all sizes create, maintain, and retrieve their business database while controlling who is allowed to access it. These systems are indispensable business tools, allowing fast and secure access to those who need it.
SAP HANA uses in-memory DBs.
SAP HANA uses an in-memory database, which means that it uses a computer’s main memory for storage rather than using hard drive storage, like most other database management systems.
The system is column-oriented, storing data in columns instead of the usual rows—this saves storage space and improves data access times.
SAP HANA Features Advanced Analytics
An RDBMS with advanced analytics capabilities can give organizations a powerful way to not only access but analyze their data, which is helpful for making informed business choices.
Advanced analytics is a class of tools that uses sophisticated techniques and tools to analyze data more quickly than traditional analytics.
Advanced analytics uses methods like:
- Machine learning
- Neural networks
- Network and cluster analysis
- Pattern matching
- Semantic analysis
- Sentiment analysis
Businesses use advanced analytics for things like:
- Making predictions
- Identifying patterns
- Generating recommendations
- Discovering deep insights in data
Advanced analytics includes predictive and prescriptive analytics.
SAP HANA’s analytic abilities include:
- Predictive analytics
- Prescriptive analytics
- Spatial data processing
- Text search and analytics
- Streaming analytics
- Graph data processing
SAP HANA Includes ETL (Extract, Load, and Transform) Capabilities
ETL takes raw data and puts it in a data system (like a data warehouse or data lake) on a target server and then prepares it for downstream uses.
ELT is composed of three data operations being performed on data:
- Extract: Extraction is the process of getting the data out of one or more source systems like databases, files, archives, ERP, CRM, or another system.
- Load: Loading is the process of putting the extracted data into the target database.
- Transform: Data transformation is converting the source data into a format which can be analyzed. Transforming data usually involves rules that define how it should be converted for use in the target data store. Data transformation can take a number of forms, but it usually involves converting coded data into usable data using lookup tables and code.
The following are examples of transformations:
- Aggregating numeric sums
- Applying mathematical functions
- Combining data from different tables and databases
- Converting data types
- Modifying text strings
- Replacing codes with values
So SAP HANA’s ETL capabilities allow it to gather data from multiple sources (and in different formats) and store it all in one database. For extraction and transfer processes up to the initial layer or for direct access to the data using different interfaces depending on the source and format of the data.
Using transformations, data is transferred from one format from the source to another format for the analytical application using the specified interfaces. The transformation consolidates, cleans up and integrates the data, synchronizing it and making it evaluable.
The History of SAP HANA
SAP HANA was developed in 2010 to provide businesses with immediate querying ability by using the world’s first-ever in-memory database. Since then, it’s become one of SAP’s most popular products, with thousands of organizations worldwide using the solution.
Since its original release, the product has come a long way. It now provides cloud-based solutions and integrating with the platforms of all of SAP’s hyperscale partners:
- Alibaba Cloud
- Amazon Web Services
- Google Cloud
- Microsoft Azure
Hyperscale storage is different than traditional enterprise storage in several ways:
- Hyperscale storage is usually software-defined, which means it’s fully automated with minimal direct human involvement.
- Hyperscale storage typically serves millions of users with only a few applications, while traditional enterprise setups usually have fewer users and more apps.
- Hyperscale storage may lack redundancy because the goal is to maximize raw storage space and minimize costs.
- A hyperscale system has a much larger storage space than a conventional system (petabytes instead of terabytes).
SAP HANA Timeline
- 2010: Pioneer version of SAP HANA limited release.
- 2011: General release unveiled at SAPPHIRE NOW technology conference.
- 2012: SAP HANA Cloud SAAS comes out.
- 2013: A Private Cloud solution, SAP HANA Enterprise Cloud service is released.
- 2013: SAP HANA XS, a lightweight app server that allows for app development, is released.
- 2015: SAP HANA 2.0, SAP S/4HANA, and SAP C/4HANA (now called SAP CX) are released.
- 2016: SAP BW/4HANA data warehouse solution comes out.
- 2019: SAP HANA Cloud Platform is rebranded as SAP Cloud Platform.
The above timeline offers a quick look at some of the biggest changes that SAP HANA’s gone through since its inception over a decade ago.
SAP’s regularly making improvements and releasing updated versions, which is how they’re able to stay at the forefront of innovative ERP technology solutions.
What Exactly Does SAP HANA Do?
Now that you know a little bit about what relational database management systems are and their role in helping a business stay organized, you might be interested to learn a little bit about what sets SAP HANA apart from the competition.
We’ve gone into how SAP HANA came to be, so the logical next step is to dive a little deeper into the system’s features.
After all, there must be some reason that this particular RDBMS is taking the business world by storm, right?
Below are laid out an examination of some of SAP HANA’s central features below so you can see exactly how it helps business operations run more smoothly.
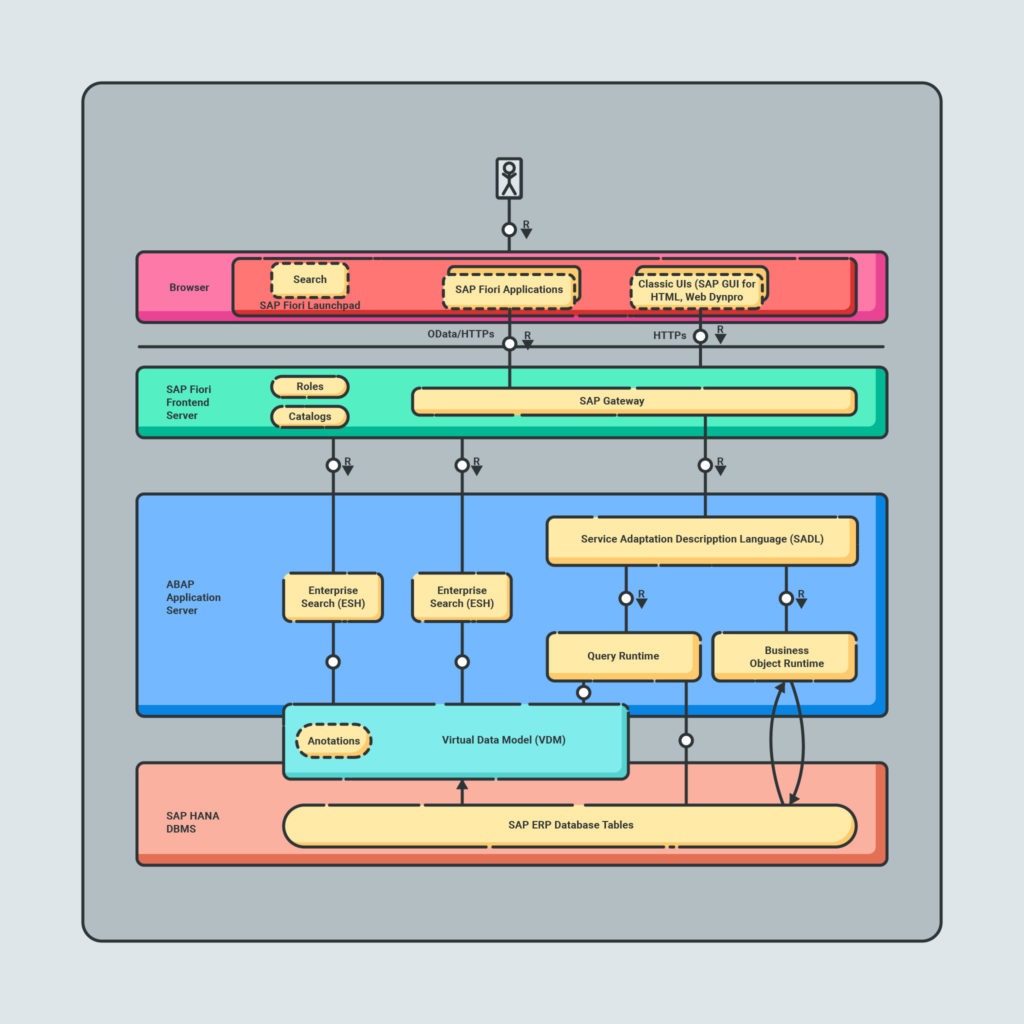
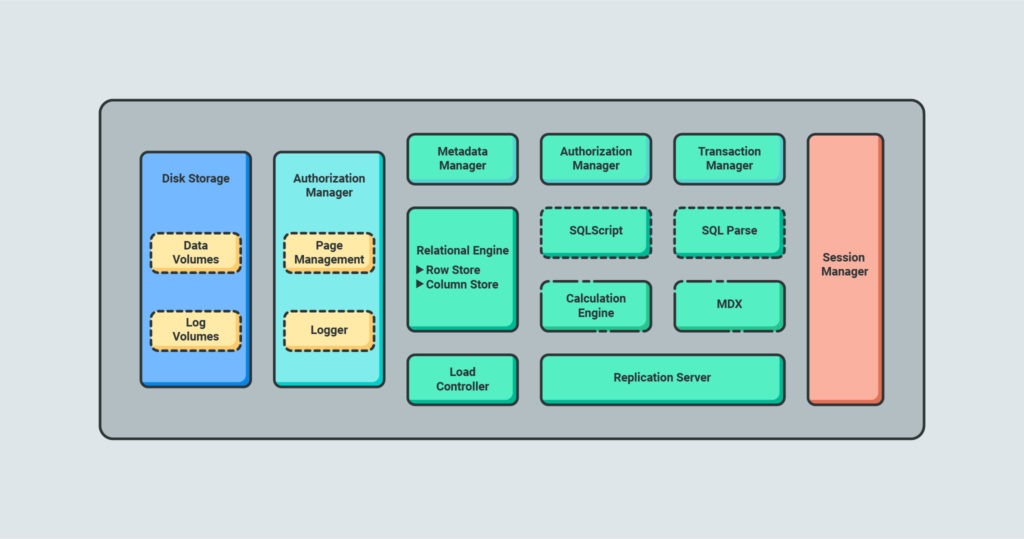
First, here’s an overview of the SAP HANA on-premise landscape and it’s three-tier architecture that’s composed of three layers:
- Presentation
- Application server
- Database
This helps you understand the general role SAP HANA plays in an SAP ERP system:
Database Storage and Management
The core feature of SAP HANA is its function as a database server, providing storage and management capabilities for databases of all sizes.
Impressively, it can store up to a petabyte of data and still return query results in less than a second.
1 PB (Petabyte) is equivalent to 1,024 TB (Terabytes) or 1 million GB (Gigabytes). 1,024 PB equals 1 EB (Exabyte) or 1 billion GB.
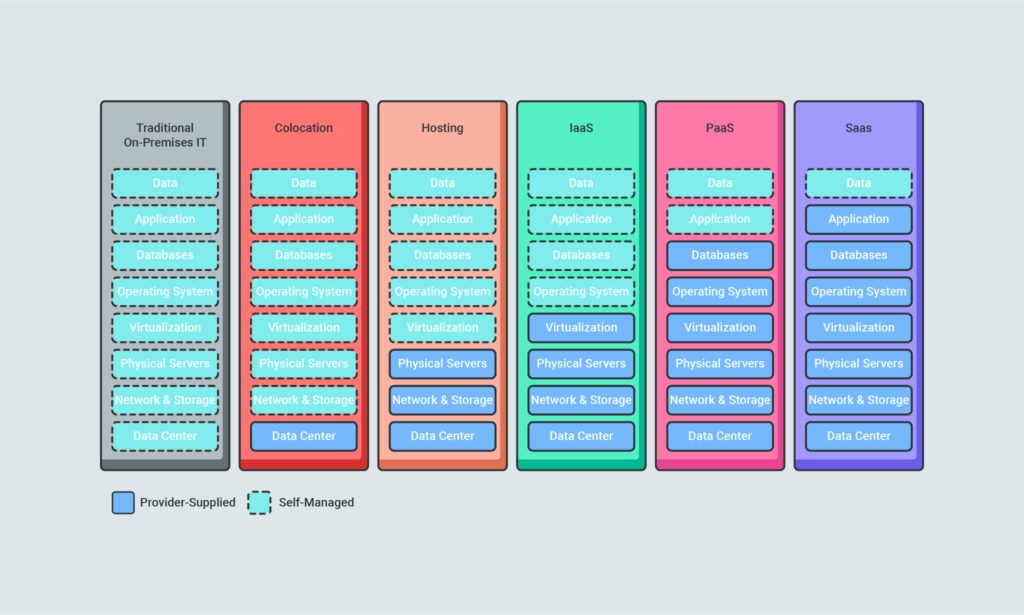
Growing organizations will appreciate the system’s scalability, which allows the server to grow with your database. There are options to store your data on-premise or in the cloud, depending on your needs. When you deploy your SAP HANA database in the cloud then it’s considered an IaaS:
Column-Oriented Database Management
How is SAP HANA able to retrieve information so quickly?
One answer is by using column-oriented database storage rather than row-oriented storage.
Column-oriented data storage speeds up queries by:
- More efficiently compressing data, so it’s faster to access
- Stacking information in columns for quicker scannability
Column-oriented storage is popular among data warehouses and other organizations that need to store and query large amounts of data.
How does a columnar database works? Let’s take a look:
Columnar databases store data as columns instead of rows. In a columnar database, a record’s values are not stored together in one row. Rather each record’s value is separately stored in a column.
So, all the column 1 values of all records are physically together, followed by all the column 2 values, and so on.
The values are stored in record order, so the 123rd entry for column 1 and the 123rd entry for column 2 belong to the same record. That lets you access a column’s values all at once, instead of row-by-row. For example, the name of a material.
With columnar storage, sequential memory locations are packed together as they contain the same types of data. So column storage has the advantage of saving disk space.
Column values are organized in a dictionary, where an ID is assigned to each value. With each item having a unique ID, operations on data are optimized. Columns work especially fast with operations like:
- Sum
- Count
- Max
- Min
A sorted dictionary is used to store the distinct values occurring in a column. The column is actually stored as a vector of value IDs and the storage structure enables you to quickly identify a position in the dictionary and find the actual data from the position.
Columnar storage makes things faster for write operations and improves performance for read operations.
Powerful Analytics
SAP understands that database management involves far more than just storing information—you must be able to access that information when needed in the blink of an eye, too.
The key to every organization’s success is the efficient use of data to:
- Identify patterns
- Predict Trends
- Learn customer behavior
- Identify procedural bottlenecks
- Make informed plans
- Spot potential problems
SAP HANA offers robust and immediate data analysis, which includes:
- Machine learning
- Predictive modeling
- Streaming analytics for live IoT data analysis
Fast, accurate, and detailed data analysis will help you and your team make smarter business decisions based on facts and figures and adjust as needed. Data analysis can help you stay ahead of trends and plan proactively instead of reacting to problems long after they’ve happened.
In-Memory Computing
How is SAP HANA able to store and process large amounts of data so efficiently? If you answered “column-oriented data storage,” that means you were paying attention; great job! But that’s not the only thing that SAP HANA has up its sleeve.
In case you haven’t already guessed by the name of this section, SAP HANA also utilizes something called in-memory computing, which was a game-changer when they came out with it over a decade ago.
In-memory computing, or in-memory processing, is just what it sounds like, with data being stored in RAM or flash memory, rather than using outdated disc-storage or relational databases. This allows access to data in real-time, so queries are completed almost instantly.
In-memory processing is hundreds of times faster than traditional memory processing and is also less expensive to maintain. Additionally, it allows users to instantly create customized reports, which is important for the use of analytics as described above.
Development Platform
Developers love SAP HANA’s web-based application server, which works with whatever language you’re familiar with:
- SQL extensions
- Javascript
- Python
- Java
- Go
- SQL script
If you’re not sure you want to deal with the hassle of integrating a new app from scratch, don’t worry—the simplified architecture allows you to create efficient and attractive applications easily.
Application development and management tools allow developers to easily deploy and monitor their apps, which can take advantage of SAP HANA’s database and analytics engines.
Data Virtualization
If you want the ability to monitor all of your business data in one place, no matter where it’s stored, then you want data virtualization. Data virtualization allows one application to retrieve data from multiple sources, regardless of its format or location.
Being able to see what’s going on with every aspect of your business all in one spot will help give you an overall view of how every aspect of the business fits together and how the different pieces are affecting one another.
SAP HANA improves data visibility in several ways.
Federation
Database federation is a form of virtual database that takes data from multiple sources and maps it together to form a single federated database.
This allows your team to query data from multiple sources and retrieve answers immediately without going through the expense or hassle of migrating everything onto one location.
Integration/Replication
SAP HANA can integrate and replicate virtually any form of data, using a combination of:
- ETL
- Replication
- Federation
HANA will be able to support your data and let you query it in real-time, regardless of the size, type, or source of the data.
Improved Quality
As any office administrator, accountant, or sales manager will attest, the most important data for any organization is accurate data.
With information being stored across multiple domains, it’s easier than ever to duplicate, miss, or contradict information. Working with badly kept records kills productivity for your team, but trying to get it all under control can be a nightmare.
HANA makes it easy to maintain and improve the quality of your data with:
- Data cleanup and duplicate removal
- Simplified data corrections
- Geolocation addition
HANA gives your team the ability to modify data across locations, all in one application.
Remote Synching
SAP HANA gives you remote access to data thanks to its two-way syncing with SAP SQL Anywhere. Now you and your team can manage data even when offline by syncing SAP SQL Anywhere to a smart or IoT device.
Administration
Database administration keeps your IT processes running smoothly, as well as keeping the data secure and available. HANA includes several administrative tools to help you manage every aspect of your database.
SAP HANA Cockpit
Remember how important it is for a business owner to see everything all in one place? Well, the SAP HANA Cockpit is that place. It allows you to monitor and manage your database and all integrated applications.
SAP HANA Studio
Administrators can use the HANA Studio to start, stop, and monitor processes and add users and permissions. Developers can use the tool to create content in SAP HANA’s repository.
SAP Solution Manager
The Solution Manager lets you monitor and run reports on all business processes and the entire landscape. This is your central alerting and monitoring tool.
SAP Landscape Manager
The Landscape Manager is where you’ll take care of maintenance and advanced HANA operations. It also allows you to automate and schedule the maintenance to take place after business hours so as not to interfere with business operations.
SAP IT Operations Analytics
As the name implies, the IT Operations Analytics center gives you a detailed insight into your data center operations. You’ll be able to resolve any datacenter issues here by collecting and analyzing the large amounts of data available in this tool.
SAP HANA hdbsql
The HANA hdbsql is a command-line tool that lets you execute SQL statements and query information. You can use this tool on a local or remote computer.
SAP HANA XS Runtime Administration
You can access the Runtime Administration tool from the cockpit and use it to adjust and maintain the runtime environment and web-based applications.
SAP HANA Application Lifecycle Management
You can install, update, and uninstall applications with the Application Lifecycle Management tool.
SAP HANA Lifecycle Manager
The Lifecycle Manager tool is where you’ll install, update, and configure your system.
SAP HANA Hardware Configuration Check Tool
You can use the Hardware Configuration Check tool to see if the hardware you’d like to add to your system is compatible.If you get a new single node system or scale-out system, this is where you’ll go to run compatibility tests and reports on it.
Types of SAP HANA Deployment
Your business can have SAP HANA installed in one of a few ways, depending on your preferences.
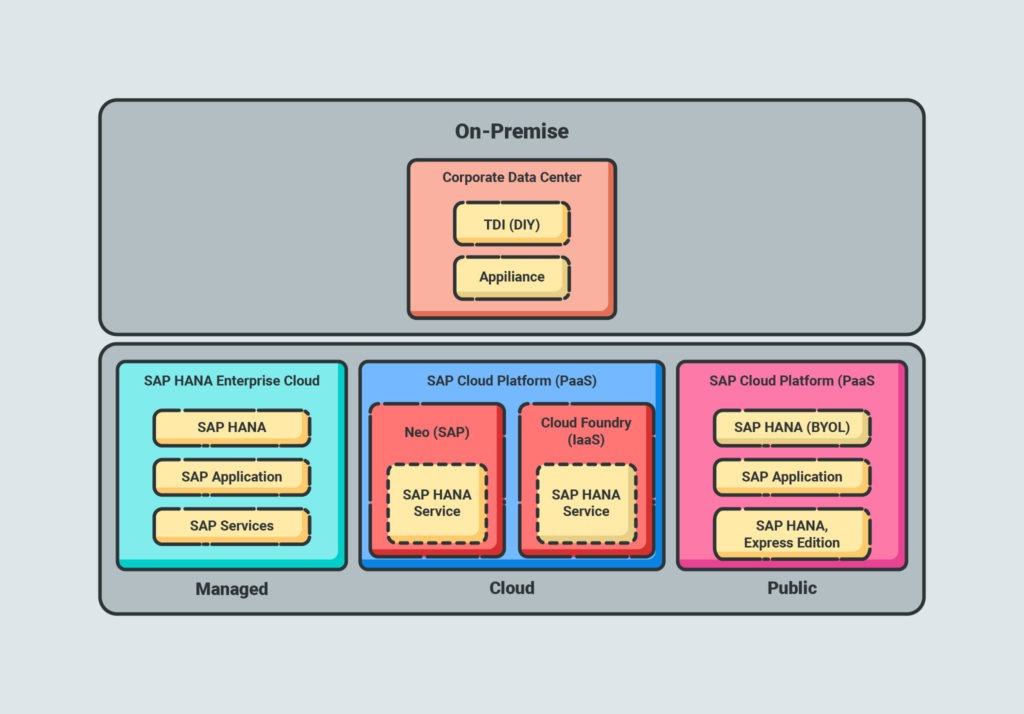
On-Premise
On-premise installation involves purchasing datacenter hardware from an authorized dealer or utilizing existing hardware and networks that you already own.
Cloud
A cloud-based system stored everything off-site using the cloud provider of your choice. There are two versions of HANA cloud deployment.
SAP HANA Cloud
The SAP HANA Cloud uses your license to store information in the public cloud. Public clouds are the most common form of cloud storage, in which the cloud is managed and hosted by a third party.
SAP HANA Enterprise Cloud
SAP HANA Enterprise Cloud is a private storage cloud that is unique to you. That means you have more options to customize it to your organization’s IT requirements, but it also means that you’re in charge of maintaining the required infrastructure to support it.
Hybrid
A hybrid or tiered deployment involves keeping your database in the cloud as well as on-premise. It’s a useful solution for businesses that want the convenience of cloud-based database management but aren’t ready to give up on-premise storage.
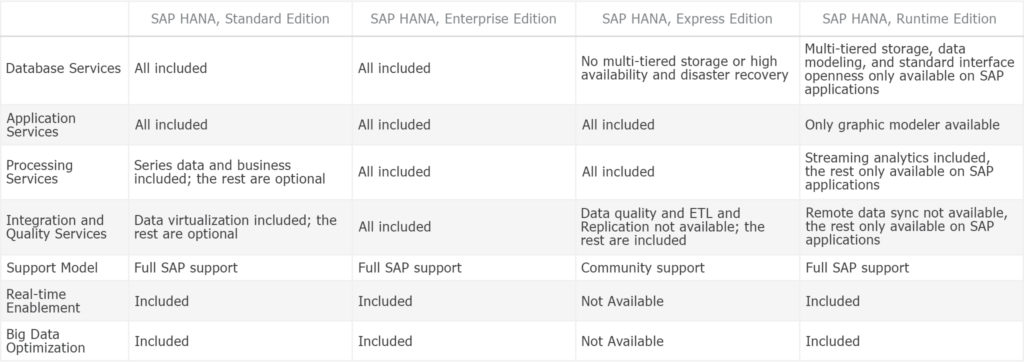
SAP HANA Version Options
SAP HANA comes in a few version options, so there’s a solution for every organization. Each one of these versions is available for cloud, on-premise, or a hybrid deployment.
The main areas where they differ can be broken down into:
- Database services
- Application services
- Processing services
- Integration and quality services
- Support model
- Real-time enablement
- Big data optimization
Let’s take a quick look at the different HANA versions. You can find more information about them here.
SAP HANA, Standard Edition
SAP HANA, Standard Edition is the most basic form of HANA, with the option to add more advanced features as needed:
- Database services: all included
- Application services: all included
- Processing services: series data and business included; the rest are optional
- Integration and quality services: data virtualization included; the rest are optional
- Support model: Full SAP support
- Real-time enablement: included
- Big data optimization: included
SAP HANA, Enterprise Edition
SAP HANA, Enterprise Edition is a robust version of HANA that takes advantage of everything HANA offers, with no restrictions:
- Database services: all included
- Application services: all included
- Processing services: all included
- Integration and quality services: all included
- Support model: Full SAP support
- Real-time enablement: included
- Big data optimization: included
SAP HANA, express edition
SAP HANA, Express Edition provides up to 32GB of database management for free, with additional features or memory available for a fee:
- Database services: no multi-tiered storage or high availability and disaster recovery
- Application services: all included
- Processing services: all included
- Integration and quality services: Data quality and ETL and Replication not available; the rest are included
- Support model: Community support
- Real-time enablement: not available
- Big data optimization: not available
SAP HANA, Runtime Edition
SAP HANA, Runtime Edition integrates with SAP applications and provides the use of limited advanced features:
- Database services: multi-tiered storage, data modeling, and standard interface openness only available on SAP applications
- Application services: only graphic modeler available
- Processing services: streaming analytics included, the rest only available on SAP applications
- Integration and quality services: remote data sync not available, the rest only available on SAP applications
- Support model: Full SAP support
- Real-time enablement: included
- Big data optimization: included
To summarize:
What Is the Cost of SAP HANA?
The cost of SAP HANA will depend on several factors, including your database’s size and which of the above options you choose for your organization. When choosing the best edition for you, keep in mind:
- Database size
- Number of licenses
- Scalability
- Adaptability
- Amount of control needed
- Integration needs
- Amount of support
Every one of these factors will influence the total amount of your SAP HANA package, but it’s always a good idea to let need influence these choices more than budget, if at all possible. You don’t want to be unhappy with your purchase because you tried to save a few dollars by buying less than you actually needed.
SAP HANA pricing is in keeping with the current cost of competing ERPs and databases. Remember that the ROI on these systems often more than offsets the initial costs.